Overview of Homeowners Insurance and Landlord Insurance
Definition of Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance is a vital safety net for individuals who own and live in their homes. It provides financial protection against various risks, including:
- Property Damage : Coverage for damages caused by fire, storms, or vandalism.
- Liability Protection : Safeguards against legal fees if someone gets injured on your property.
- Personal Property : Insures personal belongings such as furniture, electronics, and clothing.
For example, consider a homeowner who experiences a burst pipe that damages their living room; their homeowners insurance can help cover the repairs and replacements, ensuring peace of mind.
Definition of Landlord Insurance
On the other hand, landlord insurance is tailored for property owners who rent out their homes or apartments. It offers distinct coverage that homeowners insurance typically does not, such as:
- Building Coverage : Protects the physical structure against tenant-related damages.
- Loss of Rental Income : Compensation if the property becomes uninhabitable due to damage.
- Liability Protection : Extended coverage for injuries or damages occurring on the rental property.
For instance, if a tenant accidentally causes a fire that damages the property, landlord insurance can help cover the losses and repairs, ensuring landlords are not left bearing the entire financial burden.
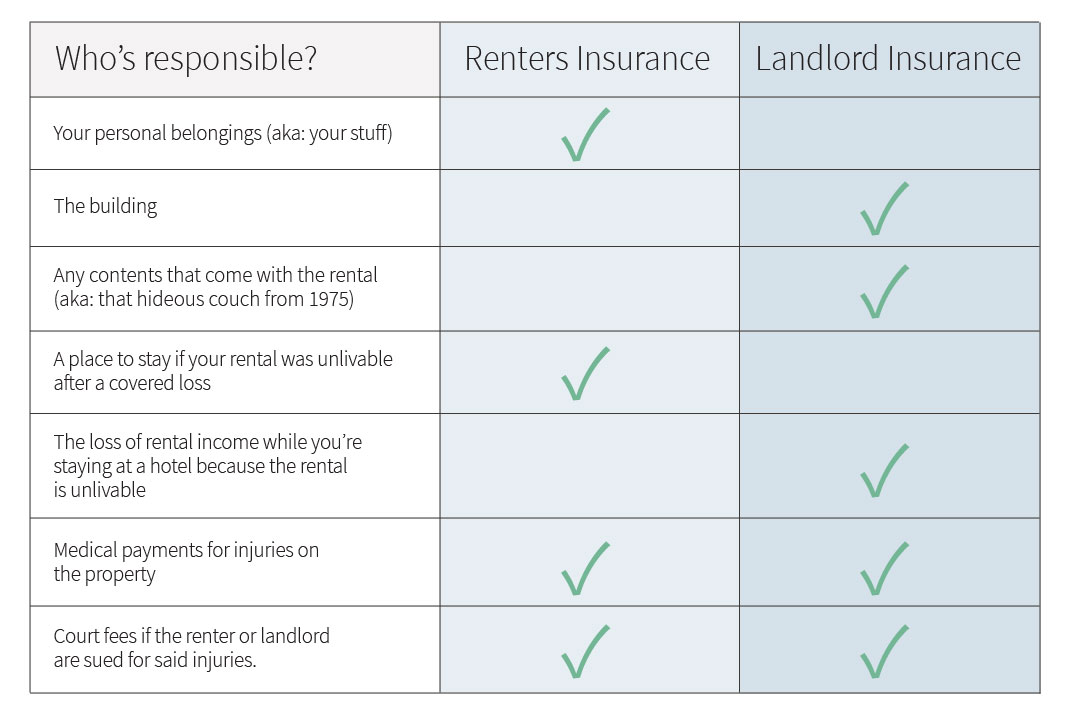
Coverage Comparison
Coverage Offered by Homeowners Insurance
When digging deeper into homeowners insurance, it’s essential to understand its comprehensive coverage options. Homeowners insurance typically includes:
- Structure Coverage : Protection for the home’s physical structure against disasters such as fire and theft.
- Personal Property Coverage : Insures belongings within the home against damage or theft.
- Liability Coverage : Financial protection against legal claims if someone gets injured on your property.
Imagine a scenario where a friend slips and falls in your living room; your homeowners insurance can help cover any medical expenses they incur, easing your worries about potential lawsuits.
Coverage Offered by Landlord Insurance
Conversely, landlord insurance focuses on the unique needs of property owners who rent out their spaces. Key coverage features include:
- Building Coverage : Protection for the rental property itself against damage from covered perils.
- Loss of Rent Coverage : Compensation for lost rental income if the unit is uninhabitable due to damages.
- Liability Coverage : Shields the landlord in cases where tenants or visitors are injured on the rental property.
For instance, if a tenant’s carelessness leads to significant damage, landlord insurance steps in, ensuring that property owners aren’t left empty-handed while repairs are underway.

Cost Differences
Factors Affecting Homeowners Insurance Cost
When it comes to homeowners insurance, several factors can influence the overall cost. These include:
- Home Location : Areas prone to natural disasters often have higher premiums.
- Home Value : The greater the replacement cost of your home, the more you’ll pay.
- Coverage Amount : More coverage means higher costs; balancing this is crucial.
- Deductibles : Opting for higher deductibles can lower premiums but increases out-of-pocket costs.
For example, a homeowner in a flood zone might pay significantly more than one in a tranquil suburb due to the perceived risks.
Factors Affecting Landlord Insurance Cost
Similarly, landlord insurance also has unique cost determinants, such as:
- Property Type : Single-family homes generally cost less to insure than multi-family units.
- Rental History : Properties with proven track records of good tenant management might attract lower premiums.
- Claims History : Frequent claims can lead to higher insurance costs.
Imagine a landlord who has never filed a claim—this could translate to more favorable rates compared to another who frequently files due to tenant damages. Understanding these factors can guide homeowners and landlords in budgeting for their insurance needs effectively.

Legal Requirements and Obligations
Legal Requirements for Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance isn’t just a smart investment—it’s often a legal necessity, especially when financing a home. Here are some essential points to keep in mind:
- Mortgage Lenders : Most lenders will require borrowers to have homeowners insurance in place before closing on a property.
- Property Laws : Some jurisdictions have regulations ensuring homeowners maintain insurance to protect against losses that could impact the neighborhood.
For instance, when purchasing a home, Jessica learned that her lender wouldn’t approve her loan without proof of coverage, emphasizing the importance of having insurance from day one.
Legal Obligations for Landlord Insurance
On the other hand, landlord insurance also comes with its own set of legal obligations:
- Local Rental Laws : Many areas require landlords to carry insurance to protect tenant safety.
- Lease Agreements : Landlords may need to outline their insurance in lease contracts, informing tenants about the coverage they have.
Take Tom, a property owner who had to present proof of insurance to comply with local regulations. By adhering to these requirements, he could legally protect both his investment and his tenants, ensuring peace of mind all around.

Making the Right Choice
Factors to Consider When Choosing Homeowners Insurance
Selecting homeowners insurance can feel overwhelming, but focusing on key factors can simplify the process:
- Coverage Needs : Evaluate the value of your home and belongings to determine adequate coverage.
- Policy Exclusions : Understand what isn’t covered; for example, some policies may not cover floods or earthquakes.
- Deductible Choices : Balance monthly premiums with a deductible you’re comfortable paying in case of a claim.
Consider Sarah, who initially chose the cheapest option but soon found it didn’t cover her area’s flood risk. By thoroughly researching her needs, she was able to find a policy that provided peace of mind.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Landlord Insurance
Landlord insurance requires its own unique considerations, including:
- Property Type : Identify coverage suited to your property type, whether it’s single-family homes or multi-unit buildings.
- Tenant Risks : Considerations for potential tenant-related damages can influence policy choices.
- Claims Support and Reputation : Look for insurers known for responsive claims services, as quick support is crucial for rental properties.
Imagine Mark, who invested time researching insurers with strong claims reputations. This foresight paid off when his property faced storm damage, allowing for a smooth claims process. By weighing these factors, both homeowners and landlords can feel confident in their insurance choices.

When Do You Need Homeowners Insurance?
Scenarios Requiring Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance is essential in several scenarios, particularly when you own a home. Key situations that necessitate having this coverage include:
- Mortgage Requirements : If you have a mortgage, lenders typically mandate homeowners insurance to protect their investment.
- Natural Disasters : In areas prone to events like hurricanes or wildfires, homeowners insurance provides critical financial protection.
- Property Damage or Theft : If your home is damaged or broken into, insurance will help cover repairs and lost valuables.
For instance, when Karen’s roof was damaged during a storm, her homeowners insurance ensured she could afford quick repairs, saving her from financial strain.
Optional Situations for Homeowners Insurance
While homeowners insurance is essential, certain scenarios allow for optional coverage considerations, such as:
- Vacant Homes : If your home is empty for an extended period, you might consider a different policy that offers specific protections.
- Seasonal Homes : For vacation or seasonal properties, tailored insurance can provide coverage without the full homeowners policy.
- Additional Coverage : Homeowners may choose to add riders for high-value items like jewelry or collectibles.
Take Mike, who owns a winter cabin. He opted for a specialized policy to protect his property during off-season months, ensuring he was fully covered while keeping costs manageable. Understanding these scenarios can help homeowners make informed decisions about their insurance needs.





